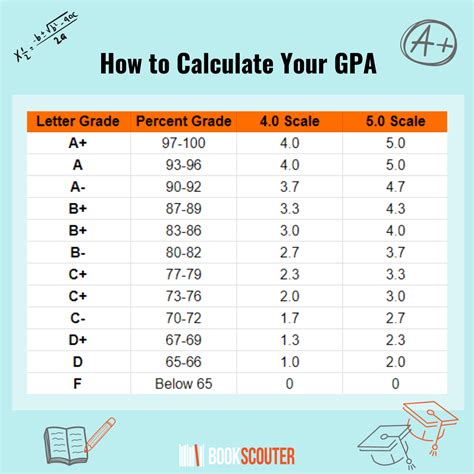
What Is A 72.500 Gpa is a figure used to quantify how a material resists deformation under load—an essential concept in materials science and engineering. In this quick explainer, we’ll break down what that number represents, how it’s measured, and what it means for design decisions.
Key Points
- The value 72.500 Gpa represents a material's stiffness, not its strength alone.
- GPa stands for gigapascals, a unit of stress commonly used in engineering.
- Measurement requires standardized tests that apply controlled loads and record deformation.
- Context matters: temperature, microstructure, and loading rate can shift effective stiffness.
- When comparing materials, ensure you compare the same test conditions and units.
What does the modulus tell you about a material?
The modulus (in GPa) is a ratio of stress to strain in the elastic region of deformation. A higher values like 72.500 Gpa indicate a material that deforms very little under a given load, which is desirable in some structural applications but not all.
Interpreting What Is A 72.500 Gpa in Context
In practice, a value of 72.500 Gpa is typical of certain ceramics or advanced composites, and it places the material somewhere between common metals and high-stiffness ceramics. When engineers see this figure, they assess it alongside other properties like toughness, density, and thermal expansion to determine suitability for a component.
How to compare 72.500 Gpa to other materials
Compare to steel (roughly 200 GPa) or aluminum (~70 GPa). A 72.500 Gpa value could mean the material is stiffer than aluminum but not as stiff as many steels, depending on the exact composition and treatment. Always check the test standard used, as different standards yield slightly different results.
Practical caveats and considerations
Elastic modulus is just one piece of the puzzle. Temperature, humidity, and long-term loading can change effective stiffness. Also, a high GPa value does not guarantee ductility or resistance to fracture; some high-modulus materials are very brittle.
What does a GPa value like 72.500 Gpa actually measure?
+It measures the material's stiffness in the elastic region, indicating how much it will elastically deform under load before permanent change occurs.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How is 72.500 Gpa determined in testing?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Tests apply controlled stress to a sample and record the resulting strain; the slope of the stress-strain curve in the elastic region gives the modulus in GPa.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Is a higher 72.500 Gpa always better for all applications?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>No. While high stiffness helps with rigidity, it can also reduce toughness. Designers balance modulus with strength, toughness, and manufacturability.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What should I check beyond the modulus when using What Is A 72.500 Gpa in a design?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Look at temperature dependence, Poisson’s ratio, density, thermal expansion, and long-term behavior under load. The modulus is part of a broader property profile.</p>
</div>
</div>
Related Terms:
- what is a 72 500 gpa
- GPA calculator
- GPA converter to 4.0 scale
- How to calculate GPA
- GPA scale